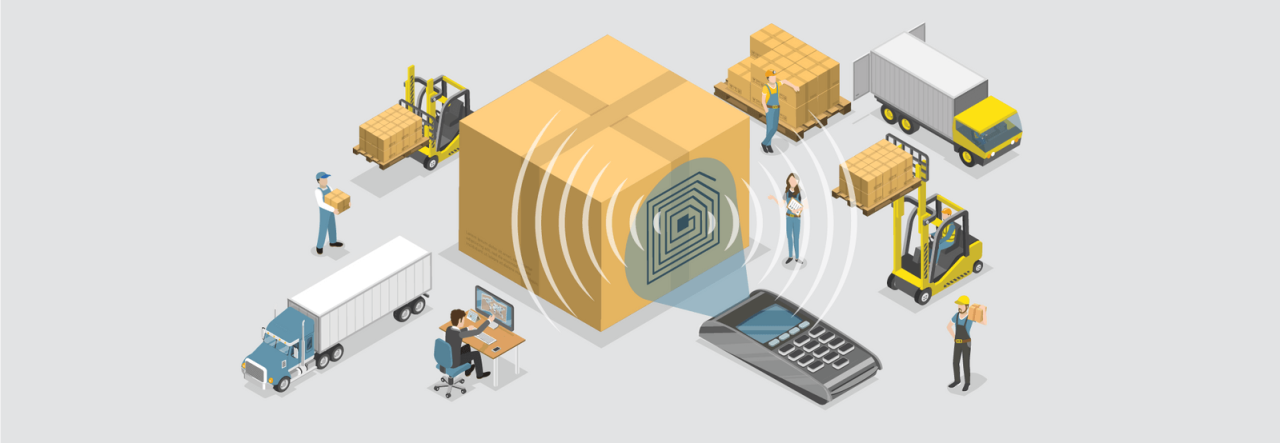
In today’s fast-paced business environment, efficient inventory management is more crucial than ever. Companies are constantly seeking ways to streamline operations, reduce costs, and enhance accuracy. One technology that has proven to be a game-changer in this realm is Radio Frequency Identification (RFID). From retail to manufacturing, RFID inventory management software is transforming how businesses manage their inventory.
What is RFID Inventory Management?
RFID inventory management involves using RFID tags and readers to automatically track and manage inventory in real-time. Unlike traditional barcoding systems, which require line-of-sight scanning, RFID tags can be read from several feet away and simultaneously, making the process much faster and more efficient.
Benefits of RFID Inventory Management Software
1. Increased Accuracy
Manual data entry and barcode scanning are prone to errors. RFID technology drastically reduces these errors by automating the inventory tracking process. This leads to more accurate stock counts and minimizes discrepancies.
2. Real-Time Tracking
One of the most significant advantages of RFID technology is the ability to track inventory in real-time. This real-time visibility allows businesses to monitor stock levels instantly, ensuring they always know what is in stock and what needs reordering. It also helps prevent stockouts and overstock situations, leading to better inventory control.
3. Enhanced Security
RFID tags can be embedded with security features that help prevent theft and unauthorized movements of goods. This added layer of security ensures that high-value items are closely monitored, reducing the risk of loss.
4. Improved Efficiency
RFID inventory management software simplifies and speeds up the inventory counting process. Employees no longer need to manually scan each item, allowing for more frequent and efficient inventory checks. This increased efficiency can lead to significant labor cost savings and improved operational productivity.
5. Better Data Insights
The data collected by RFID systems provides valuable insights into inventory patterns and trends. Businesses can leverage this data to make informed decisions about inventory purchasing, stocking strategies, and overall supply chain management. These insights can lead to more strategic planning and better resource allocation.
Industry Applications
RFID inventory management software is beneficial across various industries. In retail, it improves stock accuracy and enhances the shopping experience by ensuring that popular products are always available. In healthcare, RFID tracks medical supplies and equipment, ensuring critical items are readily accessible. Manufacturing sectors use RFID to monitor raw materials and finished goods, optimizing production processes and reducing downtime.
Conclusion
RFID inventory management software is revolutionizing how businesses manage their inventory. Its ability to provide real-time visibility, increase accuracy, enhance security, improve efficiency, and offer valuable data insights makes it an indispensable tool in modern inventory management.
For businesses looking to implement cutting-edge RFID solutions, FactorySense offers leading-edge RFID software. FactorySense’s advanced technology ensures seamless integration and superior performance, helping businesses achieve new levels of efficiency and accuracy in inventory management. Explore their innovative RFID solutions at factorysense.io.
By adopting RFID inventory management software, businesses can streamline their operations, reduce costs, and stay ahead of the competition.
Original Source: https://bit.ly/4dx6BLM
Elevate Your Operations with Advanced RFID Hardware Solutions
In today’s fast-paced industrial and commercial environments, operational efficiency is paramount. One technology that has proven to significantly enhance this efficiency is Radio Frequency Identification (RFID). With RFID hardware, from RFID consultant can streamline their processes, improve inventory management, and ensure real-time data accuracy. This article explores the different components of RFID hardware and their benefits.
RFID Tags and Labels
At the core of any RFID system are the RFID tags and labels. These small but powerful components enable seamless wireless communication with RFID readers. Engineered for durability, RFID tags and labels can withstand various environmental conditions, making them suitable for a wide range of applications. Many options are also customizable for branding, size, and encoding, providing flexibility to meet specific business needs. Whether it’s tracking goods in a warehouse or monitoring assets in a hospital, these tags provide reliable performance.
RFID Readers
To capture and process data from RFID tags, robust RFID readers are essential. Designed for extended read ranges, these readers enable efficient tag detection even in large spaces. They offer fast data capture capabilities, allowing for real-time processing and decision-making. Moreover, RFID readers are typically interoperable with a wide range of RFID tags and frequencies, ensuring versatility and compatibility across different systems. Their advanced technology supports various industries in maintaining efficient and accurate operations.
RFID Antennas
The effectiveness of an RFID system also depends on the quality of its antennas. RFID antennas ensure optimal signal transmission and extended read ranges. Available in various sizes and form factors, these antennas offer deployment flexibility to suit different operational setups. Their design ensures reliability, even in diverse and challenging conditions, making them a critical component of any robust RFID system. A well-chosen antenna can significantly enhance the performance of the entire RFID infrastructure.
RFID Printers
RFID printers integrate RFID technology with traditional printing functions. These printers offer high print resolution for clear and accurate printing, supporting various media types to cater to different application needs. By incorporating RFID technology, RFID printers not only print labels but also encode data, facilitating efficient data storage and transmission. This dual functionality streamlines the process of creating and managing RFID-enabled labels, supporting effective inventory and asset management.
RFID Hub
Centralized data management is crucial for the smooth operation of RFID systems. An RFID Hub serves as an onsite server solution, providing secure and reliable data storage. It enhances data processing speed and system scalability, ensuring that businesses can handle growing data volumes without compromising performance. This centralized hub allows for efficient management of RFID data, improving overall system efficiency.
Conclusion
Integrating RFID hardware into your operations can significantly elevate efficiency and accuracy. By leveraging advanced RFID tags and labels, readers, antennas, printers, and hubs, businesses can optimize their processes and achieve real-time visibility into their operations. For those seeking top-notch RFID hardware solutions, FactorySense offers a comprehensive range of products designed to meet diverse operational needs. To learn more about their offerings, visit FactorySense.
Original Source: https://bit.ly/3zTKcto
Elevate Your Operations with Advanced RFID Hardware Solutions
In today’s fast-paced industrial and commercial environments, operational efficiency is paramount. One technology that has proven to significantly enhance this efficiency is Radio Frequency Identification (RFID). With RFID hardware, from RFID consultant can streamline their processes, improve inventory management, and ensure real-time data accuracy. This article explores the different components of RFID hardware and their benefits.
RFID Tags and Labels
At the core of any RFID system are the RFID tags and labels. These small but powerful components enable seamless wireless communication with RFID readers. Engineered for durability, RFID tags and labels can withstand various environmental conditions, making them suitable for a wide range of applications. Many options are also customizable for branding, size, and encoding, providing flexibility to meet specific business needs. Whether it’s tracking goods in a warehouse or monitoring assets in a hospital, these tags provide reliable performance.
RFID Readers
To capture and process data from RFID tags, robust RFID readers are essential. Designed for extended read ranges, these readers enable efficient tag detection even in large spaces. They offer fast data capture capabilities, allowing for real-time processing and decision-making. Moreover, RFID readers are typically interoperable with a wide range of RFID tags and frequencies, ensuring versatility and compatibility across different systems. Their advanced technology supports various industries in maintaining efficient and accurate operations.
RFID Antennas
The effectiveness of an RFID system also depends on the quality of its antennas. RFID antennas ensure optimal signal transmission and extended read ranges. Available in various sizes and form factors, these antennas offer deployment flexibility to suit different operational setups. Their design ensures reliability, even in diverse and challenging conditions, making them a critical component of any robust RFID system. A well-chosen antenna can significantly enhance the performance of the entire RFID infrastructure.
RFID Printers
RFID printers integrate RFID technology with traditional printing functions. These printers offer high print resolution for clear and accurate printing, supporting various media types to cater to different application needs. By incorporating RFID technology, RFID printers not only print labels but also encode data, facilitating efficient data storage and transmission. This dual functionality streamlines the process of creating and managing RFID-enabled labels, supporting effective inventory and asset management.
RFID Hub
Centralized data management is crucial for the smooth operation of RFID systems. An RFID Hub serves as an onsite server solution, providing secure and reliable data storage. It enhances data processing speed and system scalability, ensuring that businesses can handle growing data volumes without compromising performance. This centralized hub allows for efficient management of RFID data, improving overall system efficiency.
Conclusion
Integrating RFID hardware into your operations can significantly elevate efficiency and accuracy. By leveraging advanced RFID tags and labels, readers, antennas, printers, and hubs, businesses can optimize their processes and achieve real-time visibility into their operations. For those seeking top-notch RFID hardware solutions, FactorySense offers a comprehensive range of products designed to meet diverse operational needs. To learn more about their offerings, visit FactorySense.
Original Source: https://bit.ly/3zTKcto
Maximizing ROI with RFID Solutions: Tips from Industry Leaders
Investing in RFID technology can offer substantial benefits, including improved efficiency, enhanced asset tracking, and streamlined operations. However, to truly maximize return on investment (ROI) with RFID solutions, businesses must follow best practices throughout implementation, maintenance, and scaling. In this article, we’ll provide actionable tips from industry leaders on how to optimize your RFID investment, using FactorySense, a leading RFID company, as a case study to illustrate successful strategies.
1. Effective Implementation
The foundation of maximizing ROI with RFID technology lies in effective implementation. Here are some key tips for ensuring a smooth setup:
Conduct a Thorough Needs Assessment: Before implementation, thoroughly assess your business needs and objectives. Identify the specific challenges you aim to address with RFID technology, such as inventory management, asset tracking, or supply chain optimization.
Choose the Right Hardware and Software: Select RFID hardware and software that align with your business requirements. This includes choosing the appropriate tags, readers, and middleware based on factors like read range, environmental conditions, and data processing capabilities.
Plan for Integration: Ensure seamless integration of RFID systems with your existing IT infrastructure. Proper integration facilitates real-time data sharing and enhances overall system efficiency.
Pilot Testing: Conduct pilot tests to identify potential issues and fine-tune the system before full-scale deployment. This step helps in mitigating risks and ensuring a more stable rollout.
2. Proactive Maintenance
Maintaining your RFID system is crucial for sustaining its performance and longevity. Consider the following best practices:
Regular System Audits: Perform regular audits to ensure all components are functioning correctly. This includes checking the condition of tags, readers, and software systems.
Firmware and Software Updates: Keep your RFID firmware and software up to date to benefit from the latest features, security patches, and performance improvements.
Training and Support: Provide ongoing training for your staff to ensure they are proficient in using the RFID system. Additionally, establish a support framework to address any technical issues promptly.
3. Strategic Scaling
As your business grows, your RFID system should scale seamlessly to meet increasing demands. Here’s how to achieve strategic scaling:
Modular Design: Opt for a modular RFID system design that allows for incremental expansions. This approach enables you to add new components or functionalities without overhauling the entire system.
Scalable Infrastructure: Ensure your IT infrastructure can handle increased data volume as more RFID tags and readers are added. Invest in scalable servers, cloud storage, and robust network solutions.
Data Analytics: Leverage data analytics to gain insights from RFID-generated data. Analyze trends, identify inefficiencies, and make informed decisions to enhance operational performance.
Case Study: FactorySense
FactorySense exemplifies how a strategic approach to RFID implementation, maintenance, and scaling can lead to significant ROI. As a leading RFID company, Factory Sense conducts thorough needs assessments and selects tailored RFID solutions, ensuring effective initial setup. Their dedication to regular system audits and updates guarantees sustained performance and longevity of the RFID system.
Furthermore, FactorySense’s modular design philosophy and scalable infrastructure allow their clients to expand their RFID systems effortlessly as their business grows. Through data analytics, they provide actionable insights that help businesses optimize operations and achieve higher efficiency.
Conclusion
Maximizing ROI with RFID solutions requires a comprehensive approach encompassing effective implementation, proactive maintenance, and strategic scaling. Factory Sense serves as a prime example of an RFID company that adheres to these best practices, leading to substantial benefits and long-term success. By following these tips, businesses can ensure their RFID investments deliver maximum value and support continuous growth.
Original Source: https://bit.ly/3xOBZWP
RFID Manufacturing Solutions: Enhancing Efficiency in Production
Enhancing efficiency is one of the best ways to create a more productive and profitable business. When it comes to manufacturing, there are many different ways to tweak workflows and processes to squeeze out more efficiency from work processes. One of the most flexible and game-changing technologies to enhance manufacturing efficiency is the use of RFID.
RFID technology utilizes radio waves to transmit data from RFID software attached to objects. This data is then read by an RFID reader and processed in a number of different ways depending on the use case. This is the same technology used in key fobs, security access cards, and even contactless payment cards.
But how exactly do RFID solutions boost productivity in manufacturing? In this post, we’re going to discuss the use of RFID manufacturing solutions, how they boost efficiency in manufacturing, and how they can be implemented.
Understanding How RFID Technology Works
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology is a form of wireless communication that uses radio waves to transmit data from an RFID-enabled tag to an RFID reader. An RFID tag can be virtually any item from a key to a plastic card. However, the important component is the microchip inside of the tag that contains a unique identification code and possibly some data.
On their own, RFID tags don’t do much because they aren’t powered by anything. In order to send data, an RFID tag must be powered by the radio waves emitted by an RFID reader. RFID readers that have been enabled will emit a field of electromagnetic energy that communicates with RFID tags but also powers them briefly so that the tag can send its unique identification code and any potential data stored in its components. In short, RFID tags are essentially useless on their own because they require an RFID reader to receive and process the data.
The RFID reader will then process the data and send it to a piece of software or another system. For example, in the context of a payment processing system, the RFID reader will read the information on the card and then use it to process a payment.
Components of an RFID System
RFID systems consist of several main components.
● RFID Tags: These contain a circuit and antenna that is protected by a casing, such as a plastic card. These tags store data and transmit it to RFID readers when they’re powered by the electromagnetic waves emitted by a reader.
● RFID Readers: Readers emit radio waves to both power and communicate with RFID tags. These readers can then transmit the data to a backend system to be stored and processed.
● RFID Software: The data accessed by an RFID reader is typically sent to a piece of software to be analyzed, collected, and processed. This can be designed to track a logistics system, store customer data, or other similar uses.
Types of RFID Tags
While the most common type of RFID tag doesn’t require power, there are actually multiple different types that could be more suitable for various situations.
● Passive RFID tags are the most common, requiring no power on the tag. These are widely used for inventory management, supply chain tracking, and access control purposes. They’re cost-effective, ideal for high-volume tagging scenarios such as manufacturing, and can be quick to deploy.
● Active RFID tags require onboard power sources, such as a battery, to enable the continuous transmission of data and also extended read and write ranges. This enables faster real-time tracking, making it suitable for keeping track of assets and vehicle identification purposes.
● Semi-Passive RFID tags work without a battery source but can have their range extended with a power source. This combines the benefits of both passive and active RFID tags but can be more costly to set up.
RFID Technology Versus Barcodes and QR Codes
RFID technology sounds similar to existing barcode systems that use patterns of black bars and white spaces that are read by a scanner. It’s also similar to modern quick-response (QR) code systems that use a two-dimensional matrix barcode. The latter was even invented to track parts in vehicle manufacturing processes.
However, RFID technology has a number of advantages over these existing systems.
● Read Range and Speed: RFID tags can be read at different distances depending on one’s needs, and they don’t require direct line-of-sight unlike barcodes and QR codes. This enables fast, efficient, and convenient scanning.
● Data Capacity: RFID tags can contain more data than barcodes and QR codes. This allows an RFID system to wirelessly transmit larger amounts of data beyond just a unique identifier or a string of text and numbers. This can include product details, manufacturing dates, maintenance records, and more. It’s even possible to send data and overwrite whatever is on an existing RFID tag.
● Durability: RFID tags are usually more durable and resistant to damage compared to barcodes and QR codes. This makes them suitable for harsh manufacturing environments.
In short, RFID tags are superior in many of the use cases where barcodes or QR codes can be used in manufacturing processes.
The Role of RFID in Manufacturing
RFID technology can address many traditional manufacturing challenges that often stem from inefficiencies that hinder productivity and profitability. It can mitigate the limitations of manual tracking and manufacturing processes, and provide real-time insights with fast and efficient data capture through RFID tag scanning.
Challenges in Traditional Manufacturing Processes
Most traditional manufacturing processes develop inefficiencies over time, resulting in challenges that can slow productivity and reduce profitability. This may include issues such as manual data entry errors, the lack of real-time analytics, and inefficient workflows which lead to bottlenecks in manufacturing processes. This can also lead to stock issues and delays which ultimately hurt a manufacturing business’s bottom line while also impacting customer satisfaction.
To address these challenges, manufacturers are turning to technology solutions such as RFID tagging to streamline operations, improve data accuracy, and identify ways in which the overall efficiency of the manufacturing process can be improved.
Addressing Challenges in Traditional Manufacturing with RFID Technology
RFID technology aims to provide effective solutions to many common manufacturing challenges. This includes, but is not limited to:
• Enhanced Asset Tracking: The best asset tracking RFID software solved a range of concerns. RFID tags can be attached to assets in order to minimize loss and prevent the need for replacements. For instance, a manufacturer could use RFID tags on components, tools, and equipment to better track their use and current location. This prevents tools and components from being misplaced, and it also enables accurate maintenance schedules and service history for each asset.
● Improved Quality Control: RFID tagging allows for real-time monitoring of materials and components as they’re transformed into finished products. It can also be used to verify the authenticity of products from trusted manufacturers, and the technology can even be used to create environmental sensors that monitor sensitive factors such as temperature, humidity, and pressure. Lastly, RFID-tagged products enable the rapid identification and recall of product batches that have been labeled with manufacturing defects, ensuring that customers don’t receive faulty products.
● Accurate inventory Management: RFID technology can help manufacturers maintain accurate inventory records which is essential for optimizing production efficiency. Automated data capture systems can keep track of raw materials and components as they’re processed into finished products, and continuous communication between RFID tags and readers allows for the real-time tracking of stock and inventory levels. These automated systems reduce the chance of manual errors, and the data can be used to identify trends in the manufacturing process. This can help point out inefficiencies in the manufacturing process and help businesses make more informed decisions.
Considerations When Implementing RFID Manufacturing Solutions
RFID manufacturing solutions are rarely simple drop-in replacements for existing systems. Implementing them requires careful planning and consideration, especially if a business wants to minimize manufacturing downtime.
Assessing Current Business Needs
Start by identifying current manufacturing needs and objectives. Determine which areas of the manufacturing process are suitable for RFID implementation, and where it can deliver the most impact. This is usually in areas such as asset tracking, quality control, and inventory management.
Analyzing Cost-Benefit
Conducting a thorough cost-benefit analysis will help evaluate the investment required for RFID implementation. This can be compared to the expected returns, giving you a much better understanding of how it could benefit your business. It’s important to consider the cost of all RFID components and implementations. This includes the tags, readers, and software infrastructure.
Infrastructure Requirements
Manufacturers will need to identify existing infrastructure challenges and determine if upgrades or modifications to existing processes and systems will be necessary before deploying RFID solutions.
Employee Training
Manufacturers will also need to provide comprehensive training to employees who will be handling RFID technology. This will need to include explaining the benefits of RFID technology, how to use and maintain RFID-enabled devices, and how the system works as a whole. Be open to addressing concerns or resistance to change, and pay close attention to employee feedback to identify challenges.
Conclusion
RFID technology introduced by the best RFID company offers transformative solutions for the manufacturing industry. It’s able to address common challenges such as inventory management and quality control and provides real-time reporting and insights to help manufacturers identify inefficiencies and make better decisions.
Original Source: https://bit.ly/45FXkyc
RFID Manufacturing Solutions: Enhancing Efficiency in Production
Enhancing efficiency is one of the best ways to create a more productive and profitable business. When it comes to manufacturing, there are many different ways to tweak workflows and processes to squeeze out more efficiency from work processes. One of the most flexible and game-changing technologies to enhance manufacturing efficiency is the use of RFID.
RFID technology utilizes radio waves to transmit data from RFID software attached to objects. This data is then read by an RFID reader and processed in a number of different ways depending on the use case. This is the same technology used in key fobs, security access cards, and even contactless payment cards.
But how exactly do RFID solutions boost productivity in manufacturing? In this post, we’re going to discuss the use of RFID manufacturing solutions, how they boost efficiency in manufacturing, and how they can be implemented.

Source: Unsplash (CC0)
Understanding How RFID Technology Works
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology is a form of wireless communication that uses radio waves to transmit data from an RFID-enabled tag to an RFID reader. An RFID tag can be virtually any item from a key to a plastic card. However, the important component is the microchip inside of the tag that contains a unique identification code and possibly some data.
On their own, RFID tags don’t do much because they aren’t powered by anything. In order to send data, an RFID tag must be powered by the radio waves emitted by an RFID reader. RFID readers that have been enabled will emit a field of electromagnetic energy that communicates with RFID tags but also powers them briefly so that the tag can send its unique identification code and any potential data stored in its components. In short, RFID tags are essentially useless on their own because they require an RFID reader to receive and process the data.
The RFID reader will then process the data and send it to a piece of software or another system. For example, in the context of a payment processing system, the RFID reader will read the information on the card and then use it to process a payment.
Components of an RFID System
RFID systems consist of several main components.
● RFID Tags: These contain a circuit and antenna that is protected by a casing, such as a plastic card. These tags store data and transmit it to RFID readers when they’re powered by the electromagnetic waves emitted by a reader.
● RFID Readers: Readers emit radio waves to both power and communicate with RFID tags. These readers can then transmit the data to a backend system to be stored and processed.
● RFID Software: The data accessed by an RFID reader is typically sent to a piece of software to be analyzed, collected, and processed. This can be designed to track a logistics system, store customer data, or other similar uses.
Types of RFID Tags
While the most common type of RFID tag doesn’t require power, there are actually multiple different types that could be more suitable for various situations.
● Passive RFID tags are the most common, requiring no power on the tag. These are widely used for inventory management, supply chain tracking, and access control purposes. They’re cost-effective, ideal for high-volume tagging scenarios such as manufacturing, and can be quick to deploy.
● Active RFID tags require onboard power sources, such as a battery, to enable the continuous transmission of data and also extended read and write ranges. This enables faster real-time tracking, making it suitable for keeping track of assets and vehicle identification purposes.
● Semi-Passive RFID tags work without a battery source but can have their range extended with a power source. This combines the benefits of both passive and active RFID tags but can be more costly to set up.
RFID Technology Versus Barcodes and QR Codes
RFID technology sounds similar to existing barcode systems that use patterns of black bars and white spaces that are read by a scanner. It’s also similar to modern quick-response (QR) code systems that use a two-dimensional matrix barcode. The latter was even invented to track parts in vehicle manufacturing processes.
However, RFID technology has a number of advantages over these existing systems.
● Read Range and Speed: RFID tags can be read at different distances depending on one’s needs, and they don’t require direct line-of-sight unlike barcodes and QR codes. This enables fast, efficient, and convenient scanning.
● Data Capacity: RFID tags can contain more data than barcodes and QR codes. This allows an RFID system to wirelessly transmit larger amounts of data beyond just a unique identifier or a string of text and numbers. This can include product details, manufacturing dates, maintenance records, and more. It’s even possible to send data and overwrite whatever is on an existing RFID tag.
● Durability: RFID tags are usually more durable and resistant to damage compared to barcodes and QR codes. This makes them suitable for harsh manufacturing environments.
In short, RFID tags are superior in many of the use cases where barcodes or QR codes can be used in manufacturing processes.
The Role of RFID in Manufacturing
RFID technology can address many traditional manufacturing challenges that often stem from inefficiencies that hinder productivity and profitability. It can mitigate the limitations of manual tracking and manufacturing processes, and provide real-time insights with fast and efficient data capture through RFID tag scanning.
Challenges in Traditional Manufacturing Processes
Most traditional manufacturing processes develop inefficiencies over time, resulting in challenges that can slow productivity and reduce profitability. This may include issues such as manual data entry errors, the lack of real-time analytics, and inefficient workflows which lead to bottlenecks in manufacturing processes. This can also lead to stock issues and delays which ultimately hurt a manufacturing business’s bottom line while also impacting customer satisfaction.
To address these challenges, manufacturers are turning to technology solutions such as RFID tagging to streamline operations, improve data accuracy, and identify ways in which the overall efficiency of the manufacturing process can be improved.
Addressing Challenges in Traditional Manufacturing with RFID Technology
RFID technology aims to provide effective solutions to many common manufacturing challenges. This includes, but is not limited to:
• Enhanced Asset Tracking: The best asset tracking RFID softwaresolved a range of concerns. RFID tags can be attached to assets in order to minimize loss and prevent the need for replacements. For instance, a manufacturer could use RFID tags on components, tools, and equipment to better track their use and current location. This prevents tools and components from being misplaced, and it also enables accurate maintenance schedules and service history for each asset.
● Improved Quality Control: RFID tagging allows for real-time monitoring of materials and components as they’re transformed into finished products. It can also be used to verify the authenticity of products from trusted manufacturers, and the technology can even be used to create environmental sensors that monitor sensitive factors such as temperature, humidity, and pressure. Lastly, RFID-tagged products enable the rapid identification and recall of product batches that have been labeled with manufacturing defects, ensuring that customers don’t receive faulty products.
● Accurate inventory Management: RFID technology can help manufacturers maintain accurate inventory records which is essential for optimizing production efficiency. Automated data capture systems can keep track of raw materials and components as they’re processed into finished products, and continuous communication between RFID tags and readers allows for the real-time tracking of stock and inventory levels. These automated systems reduce the chance of manual errors, and the data can be used to identify trends in the manufacturing process. This can help point out inefficiencies in the manufacturing process and help businesses make more informed decisions.
Considerations When Implementing RFID Manufacturing Solutions
RFID manufacturing solutions are rarely simple drop-in replacements for existing systems. Implementing them requires careful planning and consideration, especially if a business wants to minimize manufacturing downtime.
Assessing Current Business Needs
Start by identifying current manufacturing needs and objectives. Determine which areas of the manufacturing process are suitable for RFID implementation, and where it can deliver the most impact. This is usually in areas such as asset tracking, quality control, and inventory management.
Analyzing Cost-Benefit
Conducting a thorough cost-benefit analysis will help evaluate the investment required for RFID implementation. This can be compared to the expected returns, giving you a much better understanding of how it could benefit your business. It’s important to consider the cost of all RFID components and implementations. This includes the tags, readers, and software infrastructure.
Infrastructure Requirements
Manufacturers will need to identify existing infrastructure challenges and determine if upgrades or modifications to existing processes and systems will be necessary before deploying RFID solutions.
Employee Training
Manufacturers will also need to provide comprehensive training to employees who will be handling RFID technology. This will need to include explaining the benefits of RFID technology, how to use and maintain RFID-enabled devices, and how the system works as a whole. Be open to addressing concerns or resistance to change, and pay close attention to employee feedback to identify challenges.
Conclusion
RFID technology introduced by the best RFID company offers transformative solutions for the manufacturing industry. It’s able to address common challenges such as inventory management and quality control and provides real-time reporting and insights to help manufacturers identify inefficiencies and make better decisions.
Original Source: https://bit.ly/45FXkyc
Understanding How RFID Works Without Power: A Simple Guide
Understanding How RFID Works Without Power
One of the most interesting things about RFID technology is how it can work without power. When you use your credit card to pay for something, you simply hold it against a reader and it “just works”.
But there’s no battery in your credit card and you’re certainly not powering it with any kind of electricity, so how does it work? How does the microchip in your card power on, and how does it transfer data to the reader?
How Do RFID Tags Get Power?
RFID uses something known as electromagnetic induction. When an RFID reader is turned on, it emits radio waves that create an electromagnetic field around it. When an RFID tag comes in contact with this field, its antenna picks up on the radio waves, creating a small electrical current that powers the microchip in the tag. This allows it to briefly switch on and transmit stored information back to the reader.
In other words, you can think of the RFID reader as a kind of wireless power source. When it’s turned on and is actively scanning for RFID tags, it creates a field of energy that is harvested by the RFID tag to power itself.
Types of RFID Tags
There are actually several different types of RFID tags, each with their own use cases and technologies.
● Passive RFID Tags are common and do not have an internal power source. They rely on the energy from an RFID reader to operate. They’re cost-effective, lightweight, and last a very long time compared to other forms of RFID tags. They’re commonly used for inventory management, asset tracking, payment cards, and access control due to how simple and affordable they are.
● Active RFID Tags have their own power source. They usually have a battery that enables them to transmit signals over longer distances. This allows them to send data over greater distances, and they can also store and transfer more data than passive RFID tags. This makes them suitable for monitoring a fleet of vehicles, high-value assets, or large-scale logistics operations.
● Semi-Passive RFID Tags combine aspects of both passive and active RFID tags. They rely on the RFID reader’s radio waves for power but can use a small battery to boost their signal strength and functionality. They’re often used for temperature monitoring and similar sensors.
Components of an RFID System
An RFID system has several key components that work together.
● RFID Tags contain a microchip and antenna to store and transmit data. They typically don’t require a power source, but battery-powered active and semi-passive RFID tags do exist as well.
● RFID Readers emit radio waves to power RFID tags and also capture data. This is possible thanks to antennas on the RFID tags which facilitate the transmission of radio waves between the tags and readers.
● RFID Software is used to manage and process data collected from RFID systems. This can include backend systems and databases to store and analyze RFID data for various different purposes and insights.
What Are the Use Cases for RFID Tags Without Power?
RFID tags are used in many different industries. The most common use of these tags is in our credit cards and other similar plastic cards that we can use to purchase goods or pass security checks. However, there are many other uses of RFID technology, such as:
● Inventory Management: RFID tags can be placed on products for real-time tracking and inventory management purposes. The RFID tags can be read by scanners, entering the product into a system to automatically deduct it from stock. The same code can be assigned to customers and orders for a completely automated and tracked inventory management system.
● Access Control: RFID tags are frequently used for access control purposes. They can be found in access cards and security keys and used to grant access to secure areas or to open lockers and drawers. These systems can also log access to certain areas. A system can keep track of what RFID tag is used and when to create a complete security log which can be used to enhance security.
● Asset Tracking: The logistics industry makes heavy use of RFID tags to monitor the movement of various assets. Some companies keep track of containers and vehicles, while others use RFID tags to examine the movement of equipment and products. This allows someone to see exactly where their assets are, but it’s not a constant update like a GPS tracker. Instead, you’ll be able to see where the assets have checked in, like a certain vehicle or fulfilment center.
● Retail Checkout: RFID-enabled products can also be used for faster checkout processes in a retail store. These items can be scanned with RFID readers, expediting the process and reducing queue times. This leads to a much faster and more efficient shopping process for customers.
In short, RFID technology is used in a large variety of industries. It’s a fantastic piece of technology that has many practical uses, and it’s cost-effective to use as well considering the RFID tags don’t require a power source.
Conclusion
To conclude, RFID tags technically don’t work without power. The reason they don’t require a power source is because RFID readers provide the power thanks to electromagnetic induction. The readers produce a source of power which is picked up by the RFID tags to give them power. This brief amount of power is enough to send the data to the reader, thus completing the transfer.
For more information about RFID, you can rely on FactorySense.
RFID Manufacturing Solutions: Enhancing Efficiency in Production
Enhancing efficiency is one of the best ways to create a more productive and profitable business. When it comes to manufacturing, there are many different ways to tweak workflows and processes to squeeze out more efficiency from work processes. One of the most flexible and game-changing technologies to enhance manufacturing efficiency is the use of RFID.
RFID technology utilizes radio waves to transmit data from RFID tags attached to objects. This data is then read by an RFID reader and processed in a number of different ways depending on the use case. This is the same technology used in key fobs, security access cards, and even contactless payment cards.
But how exactly do RFID solutions boost productivity in manufacturing? In this post, we’re going to discuss the use of RFID manufacturing solutions, how they boost efficiency in manufacturing, and how they can be implemented.
Understanding How RFID Technology Works
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology is a form of wireless communication that uses radio waves to transmit data from an RFID-enabled tag to an RFID reader. An RFID tag can be virtually any item from a key to a plastic card. However, the important component is the microchip inside of the tag that contains a unique identification code and possibly some data.
On their own, RFID tags don’t do much because they aren’t powered by anything. In order to send data, an RFID tag must be powered by the radio waves emitted by an RFID reader. RFID readers that have been enabled will emit a field of electromagnetic energy that communicates with RFID tags but also powers them briefly so that the tag can send its unique identification code and any potential data stored in its components. In short, RFID tags are essentially useless on their own because they require an RFID reader to receive and process the data.
The RFID reader will then process the data and send it to a piece of software or another system. For example, in the context of a payment processing system, the RFID reader will read the information on the card and then use it to process a payment.
Components of an RFID System
RFID systems consist of several main components.
● RFID Tags: These contain a circuit and antenna that is protected by a casing, such as a plastic card. These tags store data and transmit it to RFID readers when they’re powered by the electromagnetic waves emitted by a reader.
● RFID Readers: Readers emit radio waves to both power and communicate with RFID tags. These readers can then transmit the data to a backend system to be stored and processed.
● RFID Software: The data accessed by an RFID reader is typically sent to a piece of software to be analyzed, collected, and processed. This can be designed to track a logistics system, store customer data, or other similar uses.
While the most common type of RFID tag doesn’t require power, there are actually multiple different types that could be more suitable for various situations.
● Passive RFID tagsare the most common, requiring no power on the tag. These are widely used for inventory management, supply chain tracking, and access control purposes. They’re cost-effective, ideal for high-volume tagging scenarios such as manufacturing, and can be quick to deploy.
● Active RFID tags require onboard power sources, such as a battery, to enable the continuous transmission of data and also extended read and write ranges. This enables faster real-time tracking, making it suitable for keeping track of assets and vehicle identification purposes.
● Semi-Passive RFID tags work without a battery source but can have their range extended with a power source. This combines the benefits of both passive and active RFID tags but can be more costly to set up.
RFID Technology Versus Barcodes and QR Codes
RFID technology sounds similar to existing barcode systems that use patterns of black bars and white spaces that are read by a scanner. It’s also similar to modern quick-response (QR) code systems that use a two-dimensional matrix barcode. The latter was even invented to track parts in vehicle manufacturing processes.
However, RFID technology has a number of advantages over these existing systems.
● Read Range and Speed: RFID tags can be read at different distances depending on one’s needs, and they don’t require direct line-of-sight unlike barcodes and QR codes. This enables fast, efficient, and convenient scanning.
● Data Capacity: RFID tags can contain more data than barcodes and QR codes. This allows an RFID system to wirelessly transmit larger amounts of data beyond just a unique identifier or a string of text and numbers. This can include product details, manufacturing dates, maintenance records, and more. It’s even possible to send data and overwrite whatever is on an existing RFID tag.
● Durability: RFID tags are usually more durable and resistant to damage compared to barcodes and QR codes. This makes them suitable for harsh manufacturing environments.
In short, RFID tags are superior in many of the use cases where barcodes or QR codes can be used in manufacturing processes.
The Role of RFID in Manufacturing
RFID technology can address many traditional manufacturing challenges that often stem from inefficiencies that hinder productivity and profitability. It can mitigate the limitations of manual tracking and manufacturing processes, and provide real-time insights with fast and efficient data capture through RFID tag scanning.
Challenges in Traditional Manufacturing Processes
Most traditional manufacturing processes develop inefficiencies over time, resulting in challenges that can slow productivity and reduce profitability. This may include issues such as manual data entry errors, the lack of real-time analytics, and inefficient workflows which lead to bottlenecks in manufacturing processes. This can also lead to stock issues and delays which ultimately hurt a manufacturing business’s bottom line while also impacting customer satisfaction.
To address these challenges, manufacturers are turning to technology solutions such as RFID tagging to streamline operations, improve data accuracy, and identify ways in which the overall efficiency of the manufacturing process can be improved.
Addressing Challenges in Traditional Manufacturing with RFID Technology
RFID technology aims to provide effective solutions to many common manufacturing challenges. This includes, but is not limited to:
● Enhanced Asset Tracking: RFID tags can be attached to assets in order to minimize loss and prevent the need for replacements. For instance, a manufacturer could use RFID tags on components, tools, and equipment to better track their use and current location. This prevents tools and components from being misplaced, and it also enables accurate maintenance schedules and service history for each asset.
● Improved Quality Control: RFID tagging allows for real-time monitoring of materials and components as they’re transformed into finished products. It can also be used to verify the authenticity of products from trusted manufacturers, and the technology can even be used to create environmental sensors that monitor sensitive factors such as temperature, humidity, and pressure. Lastly, RFID-tagged products enable the rapid identification and recall of product batches that have been labeled with manufacturing defects, ensuring that customers don’t receive faulty products.
● Accurate inventory Management: RFID technology can help manufacturers maintain accurate inventory records which is essential for optimizing production efficiency. Automated data capture systems can keep track of raw materials and components as they’re processed into finished products, and continuous communication between RFID tags and readers allows for the real-time tracking of stock and inventory levels. These automated systems reduce the chance of manual errors, and the data can be used to identify trends in the manufacturing process. This can help point out inefficiencies in the manufacturing process and help businesses make more informed decisions.
Considerations When Implementing RFID Manufacturing Solutions
RFID manufacturing solutions are rarely simple drop-in replacements for existing systems. Implementing them requires careful planning and consideration, especially if a business wants to minimize manufacturing downtime.
Assessing Current Business Needs
Start by identifying current manufacturing needs and objectives. Determine which areas of the manufacturing process are suitable for RFID implementation, and where it can deliver the most impact. This is usually in areas such as asset tracking, quality control, and inventory management.
Analyzing Cost-Benefit
Conducting a thorough cost-benefit analysis will help evaluate the investment required for RFID implementation. This can be compared to the expected returns, giving you a much better understanding of how it could benefit your business. It’s important to consider the cost of all RFID components and implementations. This includes the tags, readers, and software infrastructure.
Infrastructure Requirements
Manufacturers will need to identify existing infrastructure challenges and determine if upgrades or modifications to existing processes and systems will be necessary before deploying RFID solutions.
Employee Training
Manufacturers will also need to provide comprehensive training to employees who will be handling RFID technology. This will need to include explaining the benefits of RFID technology, how to use and maintain RFID-enabled devices, and how the system works as a whole. Be open to addressing concerns or resistance to change, and pay close attention to employee feedback to identify challenges.
Conclusion
RFID technology offers transformative solutions for the manufacturing industry. It’s able to address common challenges such as inventory management and quality control and provides real-time reporting and insights to help manufacturers identify inefficiencies and make better decisions.
To get more details about RFID solutions, rely on FactorySense
Navigating the RFID Consultancy Landscape: Finding Your Ideal Consulting Partner
Navigating the complex landscape of RFID technology isn’t just about picking the right tags and readers — it’s also about finding the perfect guide to steer your company toward success. In a world where every industrial sector is inching closer to full digital transformation, the demand for RFID consultancy services has surged. These services are not only sought after by businesses that are just starting their RFID endeavors but also by those looking to revamp their existing strategies to keep pace with the latest market trends.
Understanding the Importance of RFID Consulting
RFID consultancy is vital for companies that want to harness the power of RFID technology for inventory, supply chain, and asset management, to name a few. With the right RFID consultant, businesses can gain access to tailored solutions, expert advice, and a strategic approach to implementation that ensures long-term scalability and return on investment. But with the industry growing at such a rapid pace, how can you ensure you’ve chosen the best RFID partner for your unique needs?
Selecting the Right RFID Consultant for Your Business
Whether you’re a small operation just beginning to explore RFID’s vast possibilities or a large corporation aiming to optimize your current systems, the fundamental questions to consider when seeking an RFID expert remain the same. It’s crucial to evaluate past experiences, industry recognition, and depth of knowledge in your specific sector. A standout RFID partner is one that doesn’t just suggest solutions but also supports your business every step of the way, from strategy to execution and beyond.
For a comprehensive assessment of your RFID options and to discover how to elevate your business operations through RFID technology, look no further. In the remainder of this post, we will dissect the various dimensions that make an RFID consultant ideal, as well as the specific benefits that can be realized through a partnership with an industry leader such as FactorySense.
Diving into the World of RFID Consulting
When you’re just starting your RFID journey, understanding the intricacies of this technology can feel overwhelming. That’s why it’s so important to have an RFID consulting partner that doesn’t just guide you but also educates you along the way. This relationship should be one of collaboration and knowledge sharing, ensuring that your team is not only well-equipped to manage the RFID systems but also empowered to make informed decisions that drive performance.
However, education alone is not enough. An ideal RFID consultant must also offer hands-on support tailored to your operational setup. Think of the ideal RFID partner as an extension of your business, fully immersed in your goals and dedicated to delivering solutions that match your unique needs.
The Role of Industry Recognition in RFID Consulting
One strong indicator of a consultancy’s expertise is industry recognition, which can take the form of awards, partnerships, or client testimonials. FactorySense, for instance, has been a finalist in the RFID Journal 2024 Awards for Best Large-Scale Deployment of RFID, indicating a track record of success and innovation in the field.
It’s crucial to look for an RFID expert with a demonstrated ability to bring about positive, measurable change for its clients. When you partner with an RFID company with such accolades, you leverage their experience to fuel your own success.
Beyond Implementation: Long-Term Support Services
RFID implementation doesn’t end with equipment setup and software integration. The post-implementation phase is just as critical, demanding services and support that facilitate seamless adoption. Look for RFID companies that offer ongoing support, maintenance, and system optimization to ensure that your RFID investment continues to yield benefits after the initial buzz has passed.
Through their comprehensive suite of post-implementation services, FactorySense is a prime example of this commitment to long-term excellence.
Conclusion
Finding the right RFID partner can be a game-changer in your RFID venture. With an industry leader like FactorySense, you are not just getting RFID experts — you are gaining a strategic ally dedicated to your success. Their award-nominated, tailored to meet the unique needs of your business, are a testament to their prowess in the field.
By making a commitment to excellence in education, implementation, and post-deployment support, FactorySense stands out as a beacon in the sea of RFID consultancy services. Make the right decision for your business today, and unlock the full potential of RFID technology with a partner you can trust.
Remember, whether your consulting needs arise from compliance issues or aspirations for leaner operations, implementing RFID solutions can make all the difference. And with FactorySense, that difference could be a step ahead of the competition.
Connect with a knowledgeable RFID Consultant at FactorySense today – reach out via email at info@factorysense.com or give us a call at +1 (972) 984-7176.
Navigating the RFID Consultancy Terrain: A Guide to Selecting Your Ideal Partner
In the rapidly evolving RFID technology landscape, selecting the ideal RFID consultancy is pivotal for businesses aiming to leverage RFID solutions effectively. RFID, or Radio-Frequency Identification, is a technology that uses electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects. Its applications span across various sectors, including retail, manufacturing, healthcare, and logistics, offering an innovative way to manage inventory, track assets, and enhance operational efficiency.
However, navigating the RFID landscape can be daunting without the right guidance. An experienced RFID consultant plays a crucial role in advising businesses on the optimal use of RFID technology tailored to their specific needs. From selecting the right type of RFID tags and readers to integrating RFID systems with existing IT infrastructure, a professional consultancy can pave the way for a successful RFID implementation.
When choosing an RFID consultancy, it’s essential to consider their expertise, industry experience, and track record of successful RFID projects. A reputable RFID consultant should provide a comprehensive range of services, including initial assessments, system design, installation, testing, and ongoing support. They should be equipped to offer customized solutions that align with your business objectives, improve operational workflows, and ultimately, drive growth.By leveraging the expertise of a skilled RFID consultancy, businesses can ensure the successful implementation of RFID technology and maximize their return on investment.
In conclusion, the selection of an RFID expert consultant is a critical decision for businesses looking to harness the benefits of RFID technology. A partnership with the right consultant can effectively bridge the gap between technological potential and practical application, ensuring that RFID solutions are implemented efficiently and effectively. Recognised as a Finalist in RFID Journal’s 2024 Awards for Best Large-Scale RFID Deployment, FactorySense’s expert RFID consultants can help you successfully manage your adoption of RFID technology.
Talk to an expert RFID Consultant at FactorySense today – email us at info@factorysense.com or call us on +1 (972) 984-7176.